Poseidon Greek Sea god and one of the Olympian gods; son of Cronus and Rhea; brother of Zeus, Hades, Demeter, Hera, and Hestia; husband The Roman goddess Pomona displays her fruits of plenty in the painting by French artist Nicholas Fouche (1653-1733).
Publié le 26/01/2014
Extrait du document
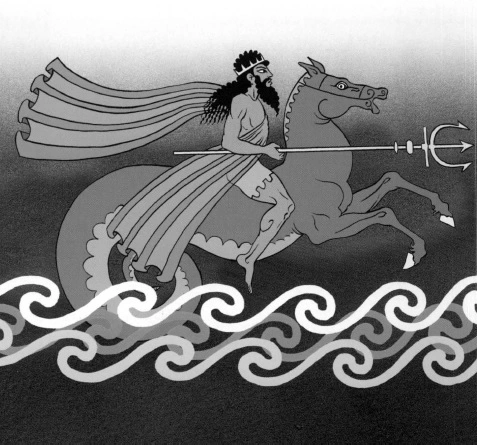

Poseidon Greek Sea god and one of the Olympian gods; son of Cronus and Rhea; brother of Zeus, Hades, Demeter, Hera, and Hestia; husband The Roman goddess Pomona displays her fruits of plenty in the painting by French artist Nicholas Fouche (1653-1733). of Amphitrite. The Romans identified Poseidon with Neptune, an Italian water god. Although Poseidon is best known as a sea god, in ancient times among migrating people he had been a god of fertility and of herdsmen. His emblem, the trident, was a symbol for the thunderbolt, which would make Poseidon a sky god of very ancient times. Some legends say that Poseidon could cause earthquakes. Like all of his siblings except Zeus, Poseidon was swallowed by his father, Cronus, and then, thanks to Zeus, later disgorged unharmed. In other legends, to save Poseidon, Rhea hid him in a flock of lambs near Mantinea, in Arcadia, in the care of a nurse named Arne. In yet another story, Rhea put Poseidon in the care of Capheira, a daughter of Oceanus, who brought up the child in Rhodes. Poseidon and Amphitrite - Mythology. Amphitrite, a nereid (sea nymph), was wooed and won for Poseidon, god of the sea, by Delphinus. In gratitude, Poseidon set the image of Delphinus among the stars as the Dolphin. Amphitrite bore Poseidon three children: Triton, Rhode, and Benthescyme. They lived in an underwater cave in Eubol, off Aegae. In its spacious stables, Poseidon kept white chariot horses with golden manes. Some people call large, white-capped waves "white horses" in memory of Poseidon's horses. Poseidon and Athene - Mythology. Poseidon was greedy for earthly kingdoms. He tried to claim the city of Athens from the goddess Athene, saying that he could do more good for the city than she could. The two appeared before a court of gods and goddesses. Poseidon struck his trident into a rock, and water immediately gushed forth, but it was seawater, salty and therefore not very useful. Athene planted the first olive tree, which gave fruit, oil, and wood. The court decreed that Athene's gift was the more beneficial and that she thus had more right to the land. The olive branch became a symbol of peace. Poseidon and Horses - Mythology. Poseidon created the horse, according to some ancient writers, with a blow of his trident. He also invented the bridle, which controls a horse. He probably started horse racing too. The horse was sacred to Poseidon. One myth has it that Poseidon changed himself into a horse to capture the love of the goddess Demeter, who had at one time transformed herself into a mare.
↓↓↓ APERÇU DU DOCUMENT ↓↓↓
Liens utiles
- Hestia (Hearth) Greek Goddess of the hearth and fire; eldest daughter of Cronus and Rhea; sister of Zeus and Hera; one of the 12 Olympian gods.
- Stheno (Strong) Greek One of the three Gorgons, female monsters; daughter of Ceto, an ancient sea goddess, and Phorcys; her sisters were Euryale and Medusa.
- Enyo (1) Greek A goddess of war, specifically known for sacking cities and towns of the enemy; daughter of Zeus and Hera; depicted as the sister, daughter, or mother of the war god Ares, often included as a companion of Ares when he went into battle.
- Euryal e (Wide-Stepping) Greek One of the three gorgons, female monsters; daughter of Ceto, an ancient sea goddess, and Phorcys; her sisters were Stheno and Medusa.
- Zeus Zeus, in Greek mythology, the god of the sky and ruler of the Olympian gods.