Ancient Egypt - history.
Publié le 26/05/2013

Extrait du document
«
The Nile River runs through the ancient city of Thebes in eastern Egypt.
For a time, beginning in 2040 bc, Thebes was the capital ofEgypt.Farrell Grehan/Photo Researchers, Inc.
According to inscriptions and documents found by archaeologists, the Egyptians called their country Kemet, meaning “the Black Land,” a reference to the dark, fertile soil that remained after the Nile floodwaters had receded.
They also used another term, Deshret, or “the Red Land,” a designation for the desert sands that burned under the blazing Sun.
In addition, they used the term Lower Egypt to refer to the northern delta area and the term Upper Egypt to refer to the communities along the river all the way south to Aswān.
The abundance of the Nile and the Egyptians’ careful management of the necessary dikes and irrigation systems guaranteed a flourishing agricultural society.
The variety ofplants that grew and were cultivated could be used for many purposes, including food, clothing, and shelter.
The river was also the source of fish, and a fishing industry wasestablished early on.
Mud from the river’s banks was the raw material for a well-established pottery industry as well as for the bricks used in construction.
To navigate theNile, the Egyptians learned to build all sorts of boats.
The land provided a wide variety of minerals, including several types of stone, semiprecious gems, salts, and metalssuch as gold, copper, and—to a much lesser extent—silver.
The Egyptians quarried, mined, and processed these resources.
Trade with other countries provided products notfound in Egypt.
III HISTORICAL FRAMEWORK
A Beginnings of Civilization
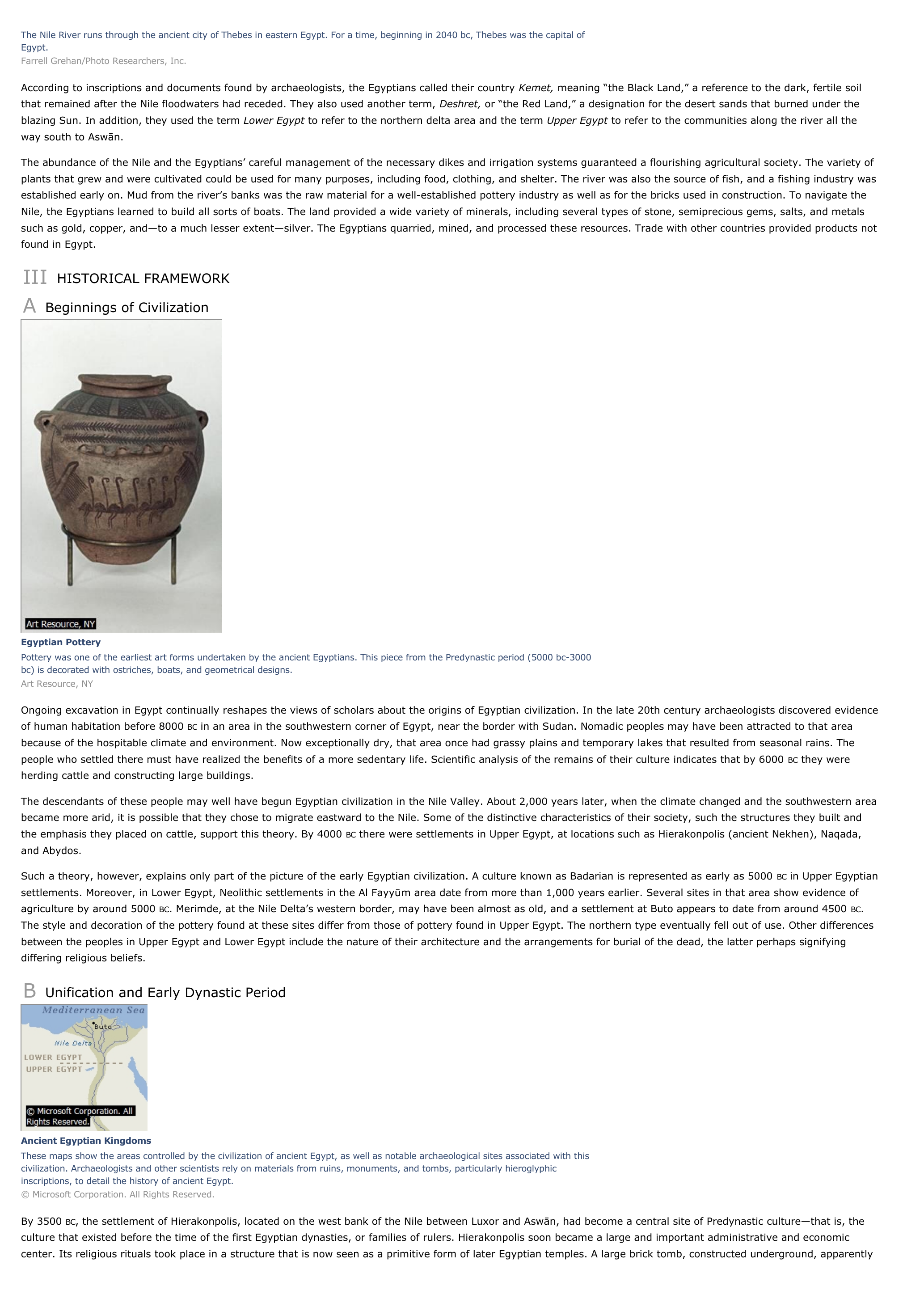
Egyptian PotteryPottery was one of the earliest art forms undertaken by the ancient Egyptians.
This piece from the Predynastic period (5000 bc-3000bc) is decorated with ostriches, boats, and geometrical designs.Art Resource, NY
Ongoing excavation in Egypt continually reshapes the views of scholars about the origins of Egyptian civilization.
In the late 20th century archaeologists discovered evidenceof human habitation before 8000 BC in an area in the southwestern corner of Egypt, near the border with Sudan.
Nomadic peoples may have been attracted to that area because of the hospitable climate and environment.
Now exceptionally dry, that area once had grassy plains and temporary lakes that resulted from seasonal rains.
Thepeople who settled there must have realized the benefits of a more sedentary life.
Scientific analysis of the remains of their culture indicates that by 6000 BC they were herding cattle and constructing large buildings.
The descendants of these people may well have begun Egyptian civilization in the Nile Valley.
About 2,000 years later, when the climate changed and the southwestern areabecame more arid, it is possible that they chose to migrate eastward to the Nile.
Some of the distinctive characteristics of their society, such the structures they built andthe emphasis they placed on cattle, support this theory.
By 4000 BC there were settlements in Upper Egypt, at locations such as Hierakonpolis (ancient Nekhen), Naqada, and Abydos.
Such a theory, however, explains only part of the picture of the early Egyptian civilization.
A culture known as Badarian is represented as early as 5000 BC in Upper Egyptian settlements.
Moreover, in Lower Egypt, Neolithic settlements in the Al Fayy ūm area date from more than 1,000 years earlier.
Several sites in that area show evidence ofagriculture by around 5000 BC.
Merimde, at the Nile Delta’s western border, may have been almost as old, and a settlement at Buto appears to date from around 4500 BC. The style and decoration of the pottery found at these sites differ from those of pottery found in Upper Egypt.
The northern type eventually fell out of use.
Other differencesbetween the peoples in Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt include the nature of their architecture and the arrangements for burial of the dead, the latter perhaps signifyingdiffering religious beliefs.
B Unification and Early Dynastic Period
Ancient Egyptian KingdomsThese maps show the areas controlled by the civilization of ancient Egypt, as well as notable archaeological sites associated with thiscivilization.
Archaeologists and other scientists rely on materials from ruins, monuments, and tombs, particularly hieroglyphicinscriptions, to detail the history of ancient Egypt.© Microsoft Corporation.
All Rights Reserved.
By 3500 BC, the settlement of Hierakonpolis, located on the west bank of the Nile between Luxor and Asw ān, had become a central site of Predynastic culture—that is, the culture that existed before the time of the first Egyptian dynasties, or families of rulers.
Hierakonpolis soon became a large and important administrative and economiccenter.
Its religious rituals took place in a structure that is now seen as a primitive form of later Egyptian temples.
A large brick tomb, constructed underground, apparently.
»
↓↓↓ APERÇU DU DOCUMENT ↓↓↓
Liens utiles
- Ancient Egypt - USA History.
- Pyramids (Egypt) - history.
- Ancient Greece - history.
- Ancient Egypt.
- Egyptian Mythology I INTRODUCTION Egyptian Mythology, specifically, the religion of ancient Egypt.