Colorado (river, North America) - geography.
Publié le 26/05/2013

Extrait du document

«
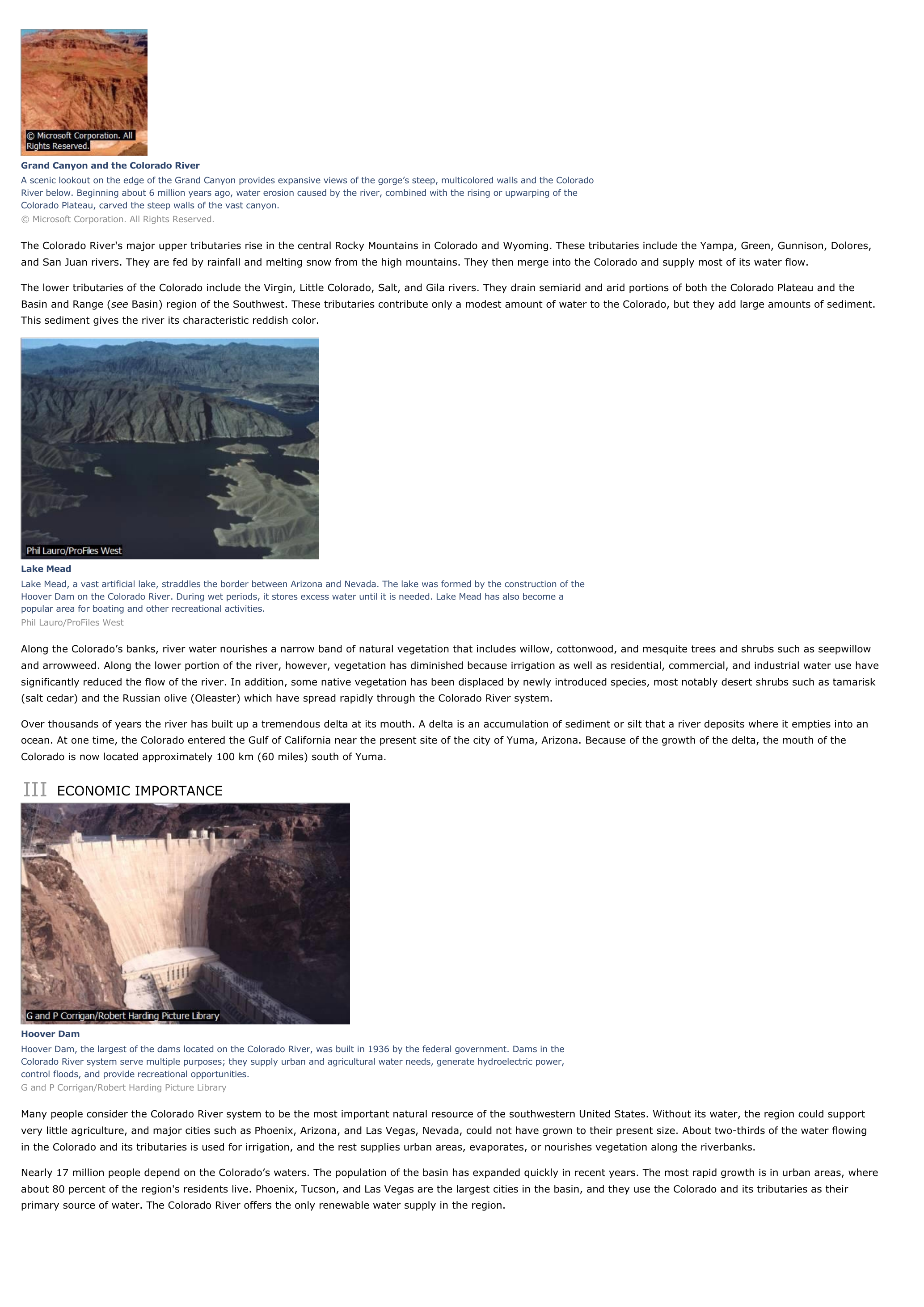
Grand Canyon and the Colorado RiverA scenic lookout on the edge of the Grand Canyon provides expansive views of the gorge’s steep, multicolored walls and the ColoradoRiver below.
Beginning about 6 million years ago, water erosion caused by the river, combined with the rising or upwarping of theColorado Plateau, carved the steep walls of the vast canyon.© Microsoft Corporation.
All Rights Reserved.
The Colorado River's major upper tributaries rise in the central Rocky Mountains in Colorado and Wyoming.
These tributaries include the Yampa, Green, Gunnison, Dolores,and San Juan rivers.
They are fed by rainfall and melting snow from the high mountains.
They then merge into the Colorado and supply most of its water flow.
The lower tributaries of the Colorado include the Virgin, Little Colorado, Salt, and Gila rivers.
They drain semiarid and arid portions of both the Colorado Plateau and theBasin and Range ( see Basin) region of the Southwest.
These tributaries contribute only a modest amount of water to the Colorado, but they add large amounts of sediment. This sediment gives the river its characteristic reddish color.
Lake MeadLake Mead, a vast artificial lake, straddles the border between Arizona and Nevada.
The lake was formed by the construction of theHoover Dam on the Colorado River.
During wet periods, it stores excess water until it is needed.
Lake Mead has also become apopular area for boating and other recreational activities.Phil Lauro/ProFiles West
Along the Colorado’s banks, river water nourishes a narrow band of natural vegetation that includes willow, cottonwood, and mesquite trees and shrubs such as seepwillowand arrowweed.
Along the lower portion of the river, however, vegetation has diminished because irrigation as well as residential, commercial, and industrial water use havesignificantly reduced the flow of the river.
In addition, some native vegetation has been displaced by newly introduced species, most notably desert shrubs such as tamarisk(salt cedar) and the Russian olive (Oleaster) which have spread rapidly through the Colorado River system.
Over thousands of years the river has built up a tremendous delta at its mouth.
A delta is an accumulation of sediment or silt that a river deposits where it empties into anocean.
At one time, the Colorado entered the Gulf of California near the present site of the city of Yuma, Arizona.
Because of the growth of the delta, the mouth of theColorado is now located approximately 100 km (60 miles) south of Yuma.
III ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE
Hoover DamHoover Dam, the largest of the dams located on the Colorado River, was built in 1936 by the federal government.
Dams in theColorado River system serve multiple purposes; they supply urban and agricultural water needs, generate hydroelectric power,control floods, and provide recreational opportunities.G and P Corrigan/Robert Harding Picture Library
Many people consider the Colorado River system to be the most important natural resource of the southwestern United States.
Without its water, the region could supportvery little agriculture, and major cities such as Phoenix, Arizona, and Las Vegas, Nevada, could not have grown to their present size.
About two-thirds of the water flowingin the Colorado and its tributaries is used for irrigation, and the rest supplies urban areas, evaporates, or nourishes vegetation along the riverbanks.
Nearly 17 million people depend on the Colorado’s waters.
The population of the basin has expanded quickly in recent years.
The most rapid growth is in urban areas, whereabout 80 percent of the region's residents live.
Phoenix, Tucson, and Las Vegas are the largest cities in the basin, and they use the Colorado and its tributaries as theirprimary source of water.
The Colorado River offers the only renewable water supply in the region..
»
↓↓↓ APERÇU DU DOCUMENT ↓↓↓
Liens utiles
- Colorado (river, North America) - Geography.
- North America - Geography.
- Religions of North America - geography.
- Languages of North America - geography.
- North America: Political - geography.