Athens (Greece) - geography.
Publié le 27/05/2013

Extrait du document
«
expected to further develop the city’s tourism industry.
Athens serves as the hub of Greece’s national transportation network.
The Greek railway system is centered in Athens, and ferries sail to the rest of the country from theport at Piraeus.
The urban area itself in Athens is served by taxis and public buses that must contend with heavily congested traffic.
The major part of the city’s metrosubway, Attiko Metro (Athens Metro), was completed in 2000 and serves the heart of Athens; extensions to residential districts are planned over the next few years.
A tramsystem under construction was expected to begin service in 2004.
Light rail will also provide a link to Eleftherios Venizelos International Airport at nearby Spáta.
Theairport, completed in 2001, replaced Ellinikon International Airport.
Economic development aid provided by the European Union (EU) has been a crucial source of funding for the city’s ongoing transportation projects.
They include theconstruction of avenues circling Athens to help relieve traffic congestion in the city center.
However, improvements to the transportation system in and around Athens oftenproceed slowly due to archaeological discoveries made during excavations and construction.
IV ANCIENT HISTORICAL SITES
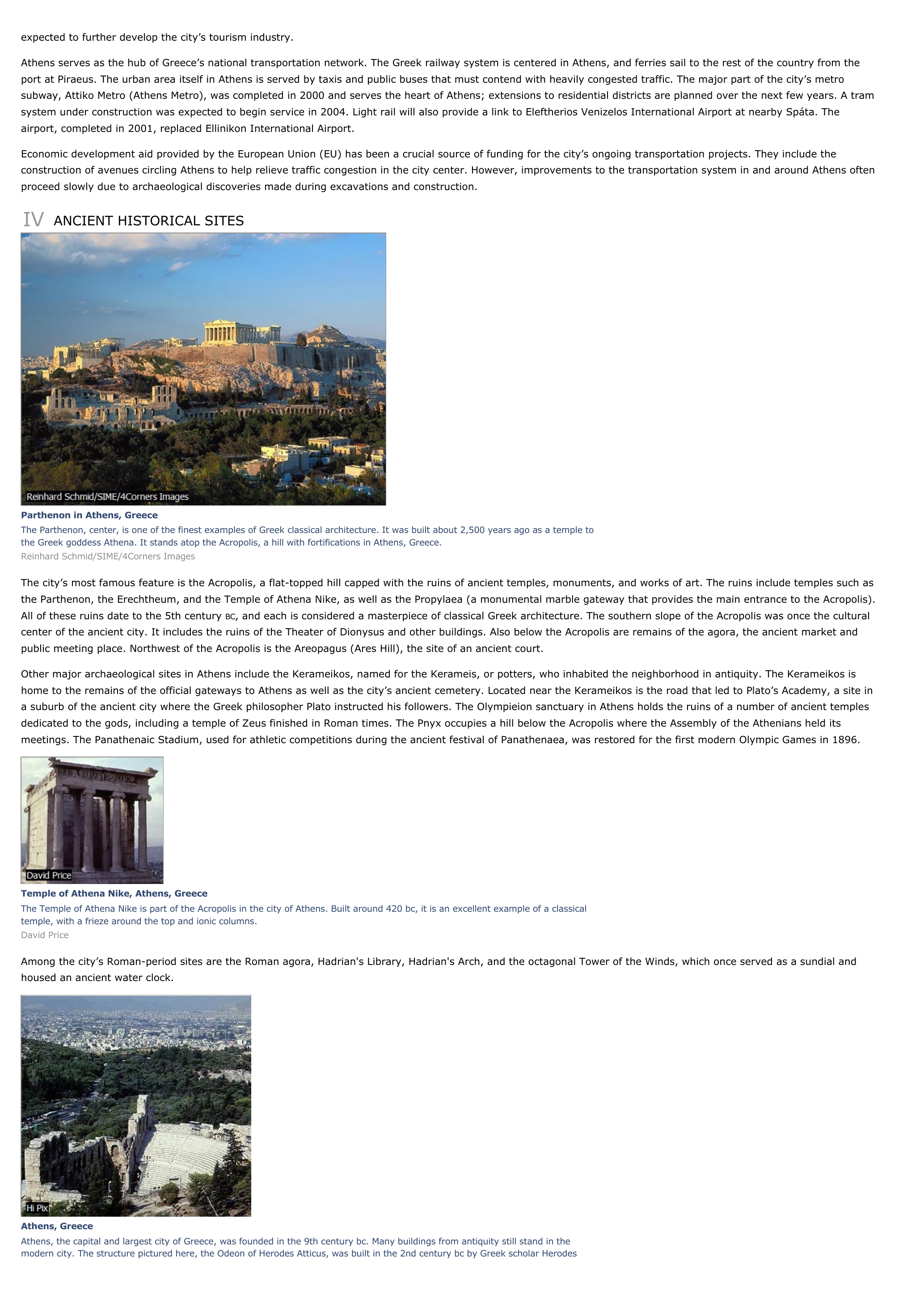
Parthenon in Athens, GreeceThe Parthenon, center, is one of the finest examples of Greek classical architecture.
It was built about 2,500 years ago as a temple tothe Greek goddess Athena.
It stands atop the Acropolis, a hill with fortifications in Athens, Greece.Reinhard Schmid/SIME/4Corners Images
The city’s most famous feature is the Acropolis, a flat-topped hill capped with the ruins of ancient temples, monuments, and works of art.
The ruins include temples such asthe Parthenon, the Erechtheum, and the Temple of Athena Nike, as well as the Propylaea (a monumental marble gateway that provides the main entrance to the Acropolis).All of these ruins date to the 5th century BC, and each is considered a masterpiece of classical Greek architecture.
The southern slope of the Acropolis was once the cultural center of the ancient city.
It includes the ruins of the Theater of Dionysus and other buildings.
Also below the Acropolis are remains of the agora, the ancient market andpublic meeting place.
Northwest of the Acropolis is the Areopagus (Ares Hill), the site of an ancient court.
Other major archaeological sites in Athens include the Kerameikos, named for the Kerameis, or potters, who inhabited the neighborhood in antiquity.
The Kerameikos ishome to the remains of the official gateways to Athens as well as the city’s ancient cemetery.
Located near the Kerameikos is the road that led to Plato’s Academy, a site ina suburb of the ancient city where the Greek philosopher Plato instructed his followers.
The Olympieion sanctuary in Athens holds the ruins of a number of ancient templesdedicated to the gods, including a temple of Zeus finished in Roman times.
The Pnyx occupies a hill below the Acropolis where the Assembly of the Athenians held itsmeetings.
The Panathenaic Stadium, used for athletic competitions during the ancient festival of Panathenaea, was restored for the first modern Olympic Games in 1896.
Temple of Athena Nike, Athens, GreeceThe Temple of Athena Nike is part of the Acropolis in the city of Athens.
Built around 420 bc, it is an excellent example of a classicaltemple, with a frieze around the top and ionic columns.David Price
Among the city’s Roman-period sites are the Roman agora, Hadrian's Library, Hadrian's Arch, and the octagonal Tower of the Winds, which once served as a sundial andhoused an ancient water clock.
Athens, GreeceAthens, the capital and largest city of Greece, was founded in the 9th century bc.
Many buildings from antiquity still stand in themodern city.
The structure pictured here, the Odeon of Herodes Atticus, was built in the 2nd century bc by Greek scholar Herodes.
»
↓↓↓ APERÇU DU DOCUMENT ↓↓↓
Liens utiles
- Athens (Greece) - geography.
- GREECE in 1996 (History and Geography)
- Ancient Greece - history.
- Ixion Greek King of the Lapiths in Thessaly, the largest ancient region of north-central Greece.
- Pythian Games Greek A sacred rite enacted in ancient Greece to honor the ancient serpentmonster, Python, slain by the god Apollo.