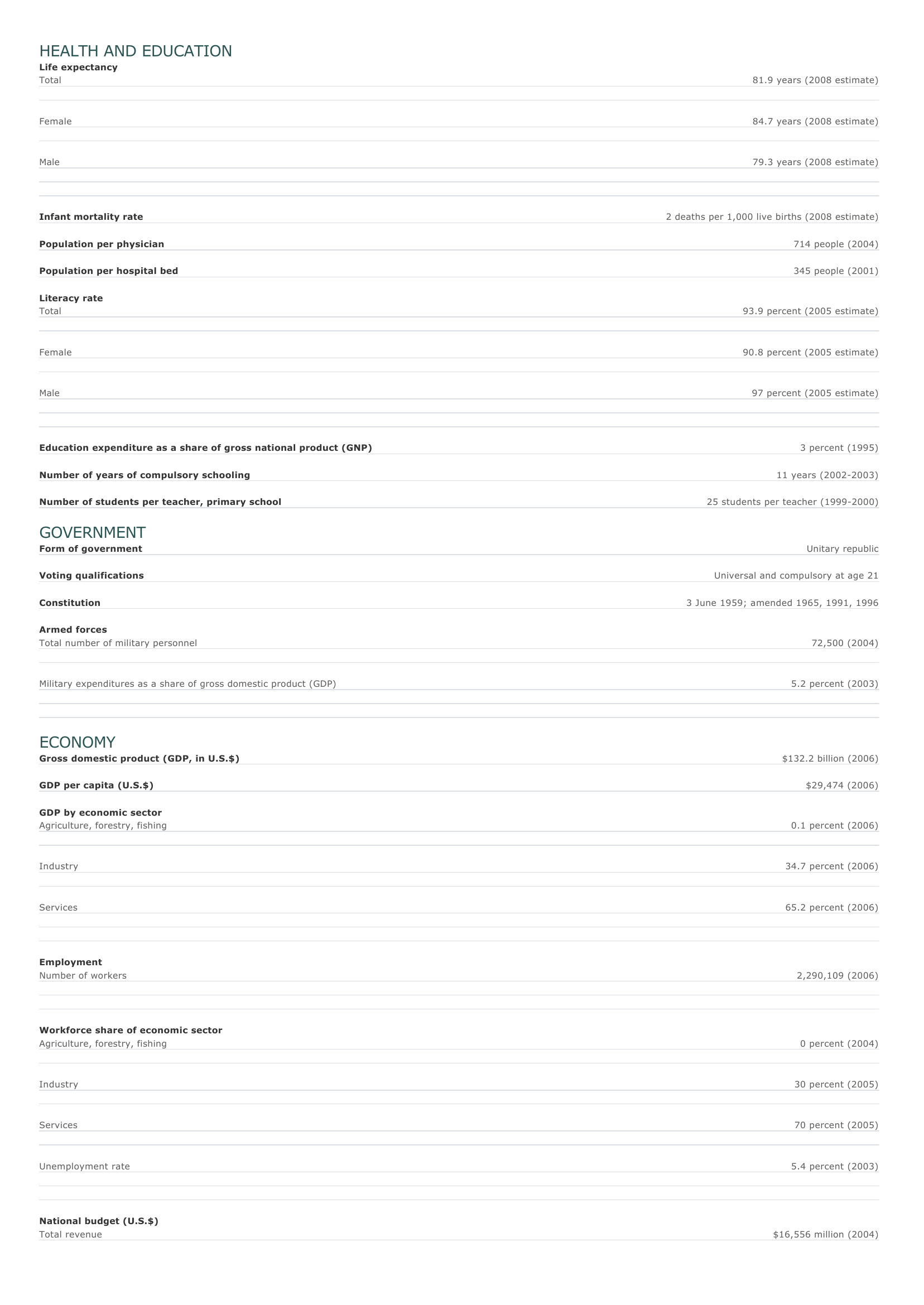
Singapore Facts and Figures. BASIC FACTS Official name Republic of Singapore Capital Singapore Area 685 sq km 265 sq mi PEOPLE Population 4,608,167 (2008 estimate) Population growth Population growth rate 1.14 percent (2008 estimate) Projected population in 2025 5,100,929 (2025 estimate) Projected population in 2050 4,635,110 (2050 estimate) Population density 17,475 persons per sq mi (2008 estimate) Urban/rural distribution Share urban Share rural 6,747 persons per sq km (2008 estimate) 100 percent (2003 estimate) 0 percent (2003 estimate) Largest cities, with population Singapore 4,608,167 (2008 estimate) Ethnic groups Chinese 77 percent Malay 14 percent I ndian 8 percent European, Japanese, other 1 percent Languages Chinese (official), Malay (official), Tamil (official), English (official) Religious affiliations Folk religions 43 percent Muslim 18 percent Buddhist 15 percent Hindu 5 percent Roman Catholic 4 percent Protestant 4 percent Nonreligious 5 percent O ther 6 percent HEALTH AND EDUCATION Life expectancy Total 81.9 years (2008 estimate) Female 84.7 years (2008 estimate) Male 79.3 years (2008 estimate) Infant mortality rate 2 deaths per 1,000 live births (2008 estimate) Population per physician 714 people (2004) Population per hospital bed 345 people (2001) Literacy rate Total 93.9 percent (2005 estimate) Female 90.8 percent (2005 estimate) Male Education expenditure as a share of gross national product (GNP) Number of years of compulsory schooling Number of students per teacher, primary school 97 percent (2005 estimate) 3 percent (1995) 11 years (2002-2003) 25 students per teacher (1999-2000) GOVERNMENT Form of government Unitary republic Voting qualifications Universal and compulsory at age 21 Constitution Armed forces Total number of military personnel Military expenditures as a share of gross domestic product (GDP) 3 June 1959; amended 1965, 1991, 1996 72,500 (2004) 5.2 percent (2003) ECONOMY Gross domestic product (GDP, in U.S.$) GDP per capita (U.S.$) GDP by economic sector Agriculture, forestry, fishing $132.2 billion (2006) $29,474 (2006) 0.1 percent (2006) I ndustry 34.7 percent (2006) Services 65.2 percent (2006) Employment Number of workers Workforce share of economic sector Agriculture, forestry, fishing 2,290,109 (2006) 0 percent (2004) I ndustry 30 percent (2005) Services 70 percent (2005) Unemployment rate 5.4 percent (2003) National budget (U.S.$) Total revenue $16,556 million (2004) Total expenditure $21,605 million (2004) Monetary unit 1 Singapore dollar (S$), consisting of 100 cents Major trade partners for exports Malaysia, United States, Hong Kong SAR, Japan, and Taiwan Major trade partners for imports Malaysia, United States, Japan, China, and Thailand ENERGY, COMMUNICATIONS, AND TRANSPORTATION Electricity production Electricity from thermal sources 100 percent (2003 estimate) Electricity from hydroelectric sources 0 percent (2003 estimate) Electricity from nuclear sources 0 percent (2003 estimate) Electricity from geothermal, solar, and wind sources 0 percent (2003 estimate) Number of radios per 1,000 people 744 (1997) Number of telephones per 1,000 people 425 (2005) Number of televisions per 1,000 people 342 (2000 estimate) Number of Internet hosts per 10,000 people 1,155 (2003) Daily newspaper circulation per 1,000 people 324 (1996) Number of motor vehicles per 1,000 people 134 (2004) Paved road as a share of total roads 100 percent (2004) SOURCES Basic Facts and People sections Area data are from the statistical bureaus of individual countries. Population, population growth rate, and population projections are from the United States Census Bureau, International Programs Center, International Data Base (IDB) (www.census.gov). Urban and rural population data are from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations (UN), FAOSTAT database (www.fao.org). Largest cities population data and political divisions data are from the statistical bureaus of individual countries. Ethnic divisions and religion data are largely from the latest Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) World Factbook and from various country censuses and reports. Language data are largely from the Ethnologue, Languages of the World, Summer Institute of Linguistics International (www.sil.org). Health and Education section Life expectancy and infant mortality data are from the United States Census Bureau, International Programs Center, International database (IDB) (www.census.gov). Population per physician and population per hospital bed data are from the World Health Organization (WHO) (www.who.int). Education data are from the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) database (www.unesco.org). Government section Government, independence, legislature, constitution, highest court, and voting qualifications data are largely from various government Web sites, the latest Europa World Yearbook, and the latest Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) World Factbook. The armed forces data is from Military Balance. Economy section Gross domestic product (GDP), GDP per capita, GDP by economic sectors, employment, and national budget data are from the World Bank database (www.worldbank.org). Monetary unit, agriculture, mining, manufacturing, exports, imports, and major trade partner information is from the statistical bureaus of individual countries, latest Europa World Yearbook, and various United Nations and International Monetary Fund (IMF) publications. Energy, Communication, and Transportation section Electricity information is from the Energy Information Administration (EIA) database (www.eia.doe.gov). Radio, telephone, television, and newspaper information is from the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) database (www.unesco.org). Internet hosts, motor vehicles, and road data are from the World Bank database (www.worldbank.org). Note Figures may not total 100 percent due to rounding. Microsoft ® Encarta ® 2009. © 1993-2008 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.