Alphabet I INTRODUCTION Bengali Script India developed a number of different writing systems over the course of its history.
Publié le 12/05/2013

Extrait du document
«
A Pictographic and Ideographic Systems
Early systems of writing used pictures to represent things and then to represent the sounds of those things.
Pictographic writing, in which a simplified picture of the sunstood for the word sun, was probably the first step toward a written language.
Chinese began as a pictographic language.
To represent abstract ideas, the Chinese writing system combined pictographs.
For example, the pictographs for sun and tree were combined to represent the concept of east.
This method of combining pictographs to represent the words for ideas is known as an ideographic system.
In written Chinese today, however, most of the characters for tangible items no longerresemble specific objects.
Pictographs and ideographs provide an inefficient system for writing: There are simply too many things to represent.
Moreover, a string of pictures cannot reproducewhat language creates: a sentence with a grammatical structure.
A crucial step in the development of writing was freeing the pictograph or ideograph from the thing itrepresented and linking it to a sound.
The ancient Sumerians generally receive credit for this advance.
B Phonetic Systems
The Sumerians began writing about 3200 BC by drawing pictures on tablets of wet clay.
In time they found it more efficient to press the pictures into the clay with a writing instrument made from a reed.
The wedge-shaped marks produced by the reed, which are now known as cuneiform, soon lost their resemblance to the originalpictures.
Because the Sumerian language was largely monosyllabic (consisting of single-syllable words), the sign for a word could equally well stand for the sound of that syllable.
Sumerian cuneiform was a mixture of word signs and syllables; some symbols served both purposes, some were simply word signs.
The Akkadians, an early Semitic people, turned cuneiform into a syllabary about 2300 BC.
Although they spoke a language unrelated to Sumerian, they adopted the syllabic sound values associated with the cuneiform wedges, without their meanings.
The Akkadians then used the wedge shapes to create a phonetic (sound-based) system for writing their own language.
Whereas each symbol carried a meaning in the Sumerian language, the symbols provided only a guide to pronunciation inAkkadian.
During the centuries after 2300 BC other Near Eastern peoples, including the Assyrians, Babylonians, and Hittites, also began using syllabic, sound-based cuneiform for writing ( see Assyro-Babylonian Language; Hittite Language).
A phonetic, or sound, system greatly reduces the number of written characters needed, because languages have only a limited number of sounds.
The change from apictographic-ideographic system to a phonetic system did not happen immediately, however.
Several ancient cultures employed both the old ideographs and the newphonetic symbols.
The ancient Egyptians created a pictographic system shortly after the Sumerians, about 3100 BC, by drawing on papyrus —a paperlike material made from the papyrus plant.
Egyptian hieroglyphs represented not only entire words but also sounds whose meanings were unrelated to the pictures.
Scholars do not knowwhether the Egyptians developed a phonetic system independently or borrowed the idea from the Sumerians.
Recent studies of the picture writing of the Maya ofMexico and Central America indicate that their system also represented syllables.
Such a word-based system becomes an alphabet (single-sound based system) orsyllabary (sound-group based system) when pictographs or ideographs are used to represent a spoken sound without an associated meaning.
In many ancient cultures the symbol for a sound came from a pictograph for a common word, signifying the word’s initial sound.
In early Semitic languages, forexample, the pictograph representing the word for house, beth in the spoken language, eventually came to represent the sound of the consonant b, the first sound in beth. This Semitic symbol, which originally stood for the entire word beth and later for the sound b, became the β of the Greek and Roman alphabets and finally the uppercase B of the English alphabet.
If English used the system of a picture to represent the first sound of a word, we might write the word sat by drawing sun + apple + table .
We would have to learn not to interpret those pictures as circle + fruit + furniture.
III THE EARLIEST ALPHABETS
Most scholars believe that the first known alphabet developed along the eastern Mediterranean coast between 1700 and 1500 BC.
Because this alphabet has not survived, scholars must draw conclusions about it from surviving alphabets that developed from it.
The people who developed this alphabet, which was known as NorthSemitic, seem to have had some knowledge of cuneiform and hieroglyphic symbols.
Some of the alphabet’s symbols may also have been taken from related writingsystems, such as those used by the Minoans and Hittites.
The sounds represented in the North Semitic alphabet consisted exclusively of consonants.
The reader had tosupply the vowel sounds of a word.
As in nearly all alphabets, the letters had names and a fixed order.
Nearly all the alphabets now used in Europe, the Middle East,and North Africa ultimately derive from the original Semitic alphabet.
A North Semitic Alphabets
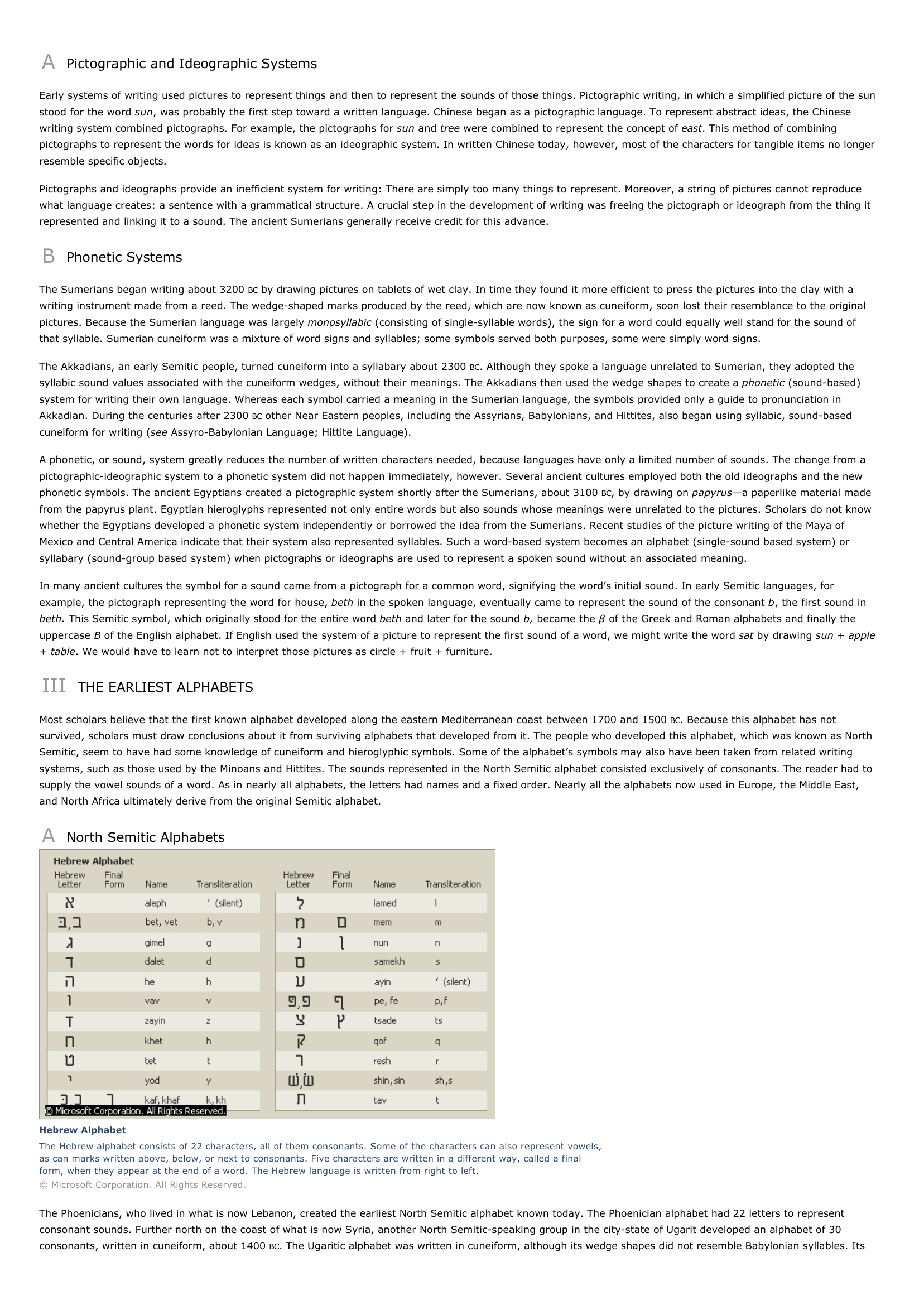
Hebrew AlphabetThe Hebrew alphabet consists of 22 characters, all of them consonants.
Some of the characters can also represent vowels,as can marks written above, below, or next to consonants.
Five characters are written in a different way, called a finalform, when they appear at the end of a word.
The Hebrew language is written from right to left.© Microsoft Corporation.
All Rights Reserved.
The Phoenicians, who lived in what is now Lebanon, created the earliest North Semitic alphabet known today.
The Phoenician alphabet had 22 letters to representconsonant sounds.
Further north on the coast of what is now Syria, another North Semitic-speaking group in the city-state of Ugarit developed an alphabet of 30consonants, written in cuneiform, about 1400 BC.
The Ugaritic alphabet was written in cuneiform, although its wedge shapes did not resemble Babylonian syllables.
Its.
»
↓↓↓ APERÇU DU DOCUMENT ↓↓↓
Liens utiles
- Number Systems I INTRODUCTION Number Systems, in mathematics, various notational systems that have been or are being used to represent the abstract quantities called numbers.
- Comedy I INTRODUCTION Laurel and Hardy Stan Laurel, in overalls, and Oliver Hardy, left, formed one of the most popular comedy teams in motion-picture history.
- William Shakespeare I INTRODUCTION William Shakespeare English playwright and poet William Shakespeare, who lived in the late 1500s and early 1600s, is regarded as the greatest dramatist in the history of English literature.
- Arthur Miller I INTRODUCTION Arthur Miller American playwright Arthur Miller began writing plays while a student at the University of Michigan.
- Charles Dickens I INTRODUCTION Charles Dickens English author Charles Dickens ranks as one of the most popular writers in the history of world literature.